Web3 applications are the future of digital innovation, reshaping how we interact online and revolutionizing the way we use technology. From enhanced user privacy to cutting-edge security measures, the world of Web3 applications is a dynamic and exciting realm waiting to be explored.
As we delve deeper into the realm of Web3 applications, we uncover a world where blockchain technology, decentralized finance, and smart contracts converge to create a new era of possibilities.
Introduction to Web3 Applications
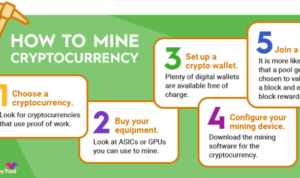
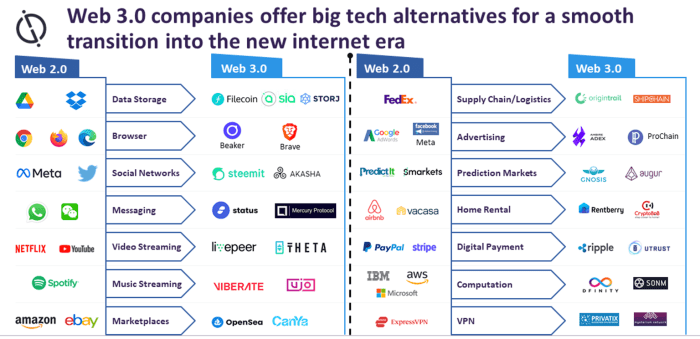
Web3 applications, also known as decentralized applications (dApps), are a new generation of applications that run on a decentralized network, such as blockchain. These applications aim to provide users with more control over their data and transactions, without the need for intermediaries.
Key Features and Characteristics of Web3 Applications
- Decentralization: Web3 applications are decentralized, meaning they operate on a distributed network of computers rather than a central server.
- Transparency: Transactions and data on Web3 applications are transparent and publicly verifiable on the blockchain.
- Security: Due to the use of blockchain technology, Web3 applications are considered to be more secure and resistant to hacking or fraud.
- Interoperability: Web3 applications can interact with each other seamlessly, allowing for greater flexibility and innovation in the digital space.
- Tokenization: Many Web3 applications use tokens or cryptocurrencies to incentivize users and facilitate transactions within the ecosystem.
Differences between Web3 and Traditional Web Applications
Web3 applications differ from traditional web applications in several ways:
- Centralization: Traditional web applications are typically centralized and rely on a central server to function, while Web3 applications are decentralized.
- Control: Users have more control over their data and digital assets in Web3 applications, whereas traditional web applications may collect and monetize user data without consent.
- Trust: Web3 applications rely on cryptographic principles and smart contracts to ensure trust and transparency, while traditional web applications may require trust in third-party intermediaries.
- Censorship Resistance: Web3 applications are more resistant to censorship and tampering, as they are not controlled by a single entity or government.
Technologies Powering Web3 Applications
Blockchain technology is at the core of Web3 applications, providing a secure and transparent way to store and manage data. This technology enables decentralized networks where information is stored across multiple nodes, ensuring data integrity and preventing single points of failure.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Impact
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, has revolutionized the financial industry by providing open access to financial services without the need for traditional intermediaries like banks. DeFi enables users to lend, borrow, trade, and earn interest on digital assets directly through smart contracts, creating a more inclusive and efficient financial system.
Smart Contracts in Web3 Applications
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically enforce and execute the terms of the agreement when predefined conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring trustless transactions. Smart contracts play a crucial role in Web3 applications by enabling automated and secure interactions between parties without relying on centralized authorities.
User Experience in Web3 Applications
User experience in Web3 applications is greatly enhanced by the focus on privacy, security, and decentralization. Let’s delve into how these aspects impact the overall user experience.
Enhanced User Data Privacy
In Web3 applications, user data privacy is significantly enhanced due to the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. Data is stored across a network of nodes, making it more secure and less susceptible to breaches or hacks. Users have more control over their personal information and can choose what data to share with applications. This increased transparency builds trust and confidence among users, leading to a better overall experience.
Decentralized User Identities
Decentralized user identities pose both challenges and benefits in Web3 applications. While the concept of owning and controlling one’s identity is empowering, managing multiple decentralized identities across different platforms can be complex. However, the benefits of increased security, privacy, and interoperability outweigh the challenges. Users have the freedom to interact with various applications without compromising their identity, leading to a seamless and secure user experience.
User Interaction with Blockchain Technology
User interaction with blockchain technology in Web3 applications is pivotal to the overall user experience. From verifying transactions to accessing decentralized applications (DApps), users engage with blockchain technology in various ways. The transparency, immutability, and security of blockchain technology enhance user trust and confidence in Web3 applications. Additionally, the seamless integration of blockchain features, such as smart contracts and tokenization, adds value and functionality to the user experience.
Security and Scalability in Web3 Applications

The security and scalability of Web3 applications are crucial aspects that need to be carefully considered for a successful and sustainable decentralized ecosystem. Security measures play a vital role in protecting user data and assets, while scalability concerns focus on the ability of the network to handle a growing number of users and transactions efficiently.
Security Measures in Web3 Applications
In Web3 applications, security is typically ensured through the use of cryptographic techniques such as public-key encryption and digital signatures. These mechanisms help to authenticate users, encrypt sensitive data, and secure transactions on the blockchain. Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, also play a significant role in ensuring trust and security within decentralized applications.
- Implementation of Multi-Signature Wallets: Utilizing multi-signature wallets require multiple parties to approve a transaction, adding an extra layer of security by preventing a single point of failure.
- Regular Security Audits: Conducting regular security audits helps identify and address vulnerabilities in the codebase before they can be exploited by malicious actors.
- Decentralized Identity Management: Implementing decentralized identity solutions helps users maintain control over their personal information and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Scalability Issues and Solutions in Web3 Applications
Scalability remains a significant challenge for Web3 applications, as blockchain networks often struggle to handle a large number of transactions simultaneously. To address this issue, developers are exploring various solutions such as layer 2 scaling solutions, sharding, and sidechains. These techniques aim to improve the throughput and performance of blockchain networks without compromising on security or decentralization.
- Layer 2 Scaling Solutions: Layer 2 solutions like state channels and sidechains enable off-chain processing of transactions, reducing the burden on the main blockchain and improving scalability.
- Sharding: Sharding involves splitting the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts called shards, allowing for parallel processing of transactions and data to increase network throughput.
- Sidechains: Sidechains are separate blockchains that run in parallel to the main blockchain, providing additional capacity for processing transactions and enabling faster and more efficient transactions.
Immutability and Data Security in Web3 Applications
Immutability is a core principle of blockchain technology that ensures once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This feature provides a high level of security and trust in Web3 applications, as it prevents unauthorized tampering with transaction history or sensitive information. By leveraging the immutability of the blockchain, developers can build secure and transparent applications that prioritize data integrity and user trust.