Supply chain management sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with American high school hip style and brimming with originality from the outset.
Get ready to dive into the intricate world of optimizing supply chains and revolutionizing business operations.
Introduction to Supply Chain Management
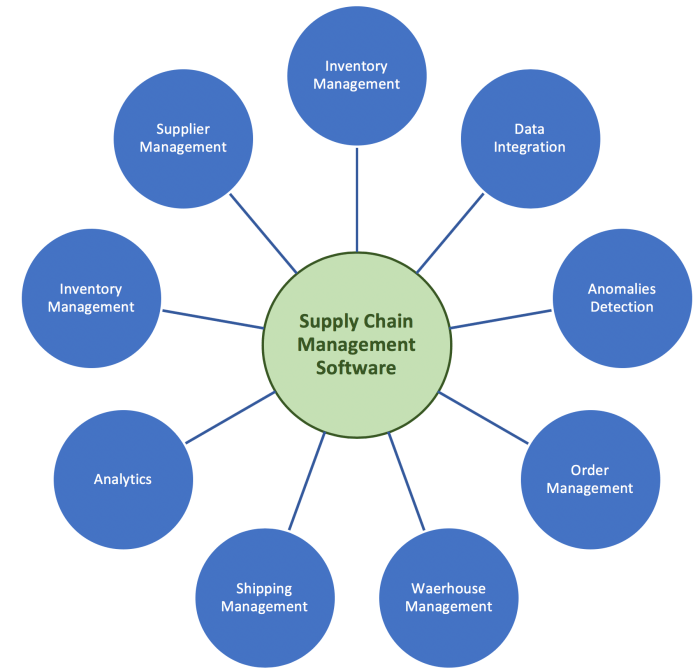
Supply chain management is the process of managing the flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the point of consumption. It involves coordinating and integrating these activities to ensure a smooth and efficient operation.
Effective supply chain management is crucial for businesses to meet customer demands, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. It helps organizations streamline their processes, minimize waste, and enhance customer satisfaction.
Key Objectives of Supply Chain Management
- Enhancing Customer Service: Supply chain management aims to deliver products and services to customers in a timely and efficient manner, meeting their expectations and enhancing satisfaction.
- Cost Reduction: By optimizing processes, reducing waste, and improving efficiency, supply chain management helps organizations lower costs and maximize profitability.
- Inventory Management: Effective supply chain management ensures that inventory levels are maintained at optimal levels to meet demand without excess or shortage, reducing carrying costs and stockouts.
- Enhancing Collaboration: Supply chain management fosters collaboration and communication among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to improve coordination and efficiency.
- Risk Management: Supply chain management helps organizations identify and mitigate risks such as disruptions, delays, and quality issues, ensuring continuity of operations.
Key Components of Supply Chain Management
Supply chain management consists of several key components that work together to ensure the smooth flow of goods and services from the point of origin to the final consumer. Each component plays a crucial role in optimizing operations and maximizing efficiency.
Supplier Management
Supplier management involves selecting, evaluating, and developing relationships with suppliers to ensure a reliable and cost-effective source of materials or products. By working closely with suppliers, companies can improve quality, reduce lead times, and minimize costs.
Inventory Management
Inventory management focuses on monitoring and controlling the flow of goods within a supply chain. It involves maintaining optimal inventory levels to meet customer demand while minimizing holding costs and stockouts. Efficient inventory management helps companies reduce waste and improve cash flow.
Logistics Management
Logistics management encompasses the planning, implementation, and control of the movement and storage of goods within a supply chain. This includes transportation, warehousing, and distribution activities. Effective logistics management ensures timely delivery of products to customers while minimizing transportation costs.
Demand Forecasting
Demand forecasting involves predicting future customer demand for products or services. By accurately forecasting demand, companies can optimize production schedules, inventory levels, and resource allocation. This helps prevent stockouts and excess inventory, leading to improved customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
Information Technology (IT) Systems
Information technology systems play a vital role in enabling seamless communication and collaboration within a supply chain. IT systems help track inventory levels, monitor supplier performance, and analyze data to identify areas for improvement. By leveraging technology, companies can streamline operations and enhance decision-making processes.
Supply Chain Strategies
In the world of supply chain management, companies often rely on different strategies to optimize their operations and meet customer demands effectively. Three common supply chain strategies include lean, agile, and responsive approaches.
Lean Strategy
The lean strategy focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency in the supply chain. Companies following this approach aim to reduce excess inventory, eliminate non-value-added activities, and streamline processes to deliver products or services to customers as efficiently as possible.
Agile Strategy, Supply chain management
The agile strategy emphasizes flexibility and quick response to changes in customer demands or market conditions. Companies adopting this approach prioritize adaptability, collaboration, and innovation to adjust production and distribution processes rapidly to meet evolving needs.
Responsive Strategy
The responsive strategy combines elements of both lean and agile strategies to create a balanced approach. Companies utilizing this strategy aim to be efficient in their operations while also maintaining the ability to respond quickly to unexpected disruptions or shifts in demand. By leveraging technology and data analytics, organizations can enhance visibility and coordination across the supply chain to improve overall performance.
Each supply chain strategy has its strengths and weaknesses, and companies must carefully evaluate their unique requirements to choose the most suitable approach. Factors such as industry dynamics, market trends, customer expectations, and operational capabilities play a crucial role in determining the optimal supply chain strategy for a business. By aligning their strategy with specific goals and objectives, companies can enhance competitiveness, reduce costs, improve customer satisfaction, and drive sustainable growth in the long run.
Technology and Innovation in Supply Chain Management
In today’s fast-paced business environment, technology plays a crucial role in the success of supply chain management. Innovations like IoT, AI, and blockchain have revolutionized the way companies manage their supply chains, leading to increased efficiency, transparency, and flexibility.
Internet of Things (IoT) in Supply Chain Management
The Internet of Things (IoT) has enabled companies to track and monitor their inventory in real-time, leading to better demand forecasting and inventory management. By using sensors and connected devices, companies can optimize their supply chain operations and reduce costs significantly.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Supply Chain Management
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming supply chains by automating repetitive tasks, analyzing data to identify patterns, and making predictive insights. AI-powered systems can optimize routes, predict maintenance needs, and enhance decision-making processes, ultimately improving overall supply chain performance.
Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain technology has introduced greater transparency and security into supply chains by creating an immutable ledger of transactions. Companies can use blockchain to track products from their origin to the final destination, ensuring authenticity and minimizing the risk of fraud or counterfeiting.
Risk Management in Supply Chains
When it comes to supply chain management, dealing with risks is crucial to ensure smooth operations and minimize disruptions. Let’s dive into the common risks in supply chains and explore strategies to mitigate them, highlighting the importance of resilience and flexibility in managing these risks.
Common Risks in Supply Chain Management
In the world of supply chains, there are several common risks that organizations need to be aware of:
- Supplier Reliability: Dependence on a single supplier can lead to disruptions if they face issues.
- Logistical Challenges: Delays in transportation or unexpected events can impact the flow of goods.
- Demand Fluctuations: Sudden changes in demand can result in excess inventory or stockouts.
- Natural Disasters: Events like earthquakes or hurricanes can disrupt supply chains.
- Cybersecurity Threats: With increasing digitalization, cyber attacks can compromise sensitive data.
Strategies to Mitigate Supply Chain Risks
To address these risks effectively, organizations can implement the following strategies:
- Diversification: Working with multiple suppliers can reduce the impact of a single supplier failure.
- Technology Integration: Utilizing supply chain management software can enhance visibility and control.
- Collaboration: Building strong relationships with partners can lead to better communication and coordination.
- Risk Assessment: Conducting regular risk assessments can help identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Resilience Planning: Developing contingency plans for various scenarios can improve response to disruptions.
Importance of Resilience and Flexibility
Resilience and flexibility are key attributes in supply chain risk management:
- Resilience allows organizations to bounce back quickly from disruptions and continue operations.
- Flexibility enables companies to adapt to changing circumstances and adjust their strategies accordingly.
- By prioritizing resilience and flexibility, organizations can build a robust supply chain that can withstand various challenges.
Sustainable Practices in Supply Chain Management
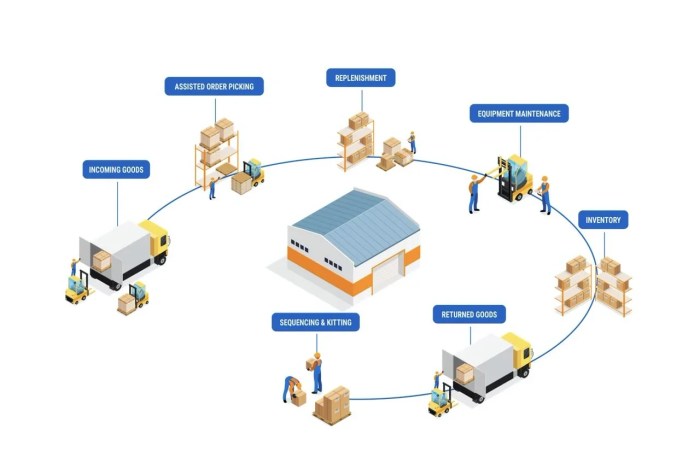
Sustainability in supply chain management refers to the integration of environmentally friendly practices, social responsibility, and economic viability throughout the entire supply chain process. It involves making decisions and implementing strategies that minimize negative impacts on the environment, society, and economy while maximizing long-term benefits.
Examples of Sustainable Practices
- Using renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power in manufacturing facilities and distribution centers to reduce carbon emissions.
- Implementing green packaging solutions to minimize waste and promote recycling.
- Partnering with suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and ethical standards.
- Optimizing transportation routes to reduce fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Benefits of Incorporating Sustainability
- Cost savings through reduced energy consumption and waste management.
- Enhanced brand reputation and customer loyalty by demonstrating commitment to environmental and social responsibility.
- Risk mitigation by anticipating and addressing potential regulatory changes related to sustainability.
- Long-term resilience and competitiveness in the market by adapting to changing consumer preferences for sustainable products and practices.